 Microorganisms exist as either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. The prokaryotic cells are morphologically much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The prokaryotic cells lack internal membrane bound organelles that are present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells such as mitochondria and chloroplast etc. Though simple, prokaryotic cell contains a variety of structures, however, all the structures are not found in every prokaryotic organism, A prokaryotic cell is bounded by a chemically complex cell wall. A cell membrane lies below the cell wall and surrounds the inner cytoplasmic matrix. This cytoplasmic matrix include unbounded nucleoid, ribosomes and some inclusion bodies. External to the cell wall there occurs extra components possessing different functions. The most typical example for prokaryotic cell organization is the bacterial cell. Structurally a bacterial cell consists of Structures external to the cell wall, cell wall and structures internal to the cell wall.
Microorganisms exist as either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. The prokaryotic cells are morphologically much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The prokaryotic cells lack internal membrane bound organelles that are present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells such as mitochondria and chloroplast etc. Though simple, prokaryotic cell contains a variety of structures, however, all the structures are not found in every prokaryotic organism, A prokaryotic cell is bounded by a chemically complex cell wall. A cell membrane lies below the cell wall and surrounds the inner cytoplasmic matrix. This cytoplasmic matrix include unbounded nucleoid, ribosomes and some inclusion bodies. External to the cell wall there occurs extra components possessing different functions. The most typical example for prokaryotic cell organization is the bacterial cell. Structurally a bacterial cell consists of Structures external to the cell wall, cell wall and structures internal to the cell wall.
1
 Microorganisms exist as either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. The prokaryotic cells are morphologically much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The prokaryotic cells lack internal membrane bound organelles that are present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells such as mitochondria and chloroplast etc. Though simple, prokaryotic cell contains a variety of structures, however, all the structures are not found in every prokaryotic organism, A prokaryotic cell is bounded by a chemically complex cell wall. A cell membrane lies below the cell wall and surrounds the inner cytoplasmic matrix. This cytoplasmic matrix include unbounded nucleoid, ribosomes and some inclusion bodies. External to the cell wall there occurs extra components possessing different functions. The most typical example for prokaryotic cell organization is the bacterial cell. Structurally a bacterial cell consists of Structures external to the cell wall, cell wall and structures internal to the cell wall.
Leia Mais
Microorganisms exist as either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. The prokaryotic cells are morphologically much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The prokaryotic cells lack internal membrane bound organelles that are present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells such as mitochondria and chloroplast etc. Though simple, prokaryotic cell contains a variety of structures, however, all the structures are not found in every prokaryotic organism, A prokaryotic cell is bounded by a chemically complex cell wall. A cell membrane lies below the cell wall and surrounds the inner cytoplasmic matrix. This cytoplasmic matrix include unbounded nucleoid, ribosomes and some inclusion bodies. External to the cell wall there occurs extra components possessing different functions. The most typical example for prokaryotic cell organization is the bacterial cell. Structurally a bacterial cell consists of Structures external to the cell wall, cell wall and structures internal to the cell wall.
Leia Mais
ULTRA STRUCTURE OF BACTERIAL CELL
 Microorganisms exist as either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. The prokaryotic cells are morphologically much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The prokaryotic cells lack internal membrane bound organelles that are present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells such as mitochondria and chloroplast etc. Though simple, prokaryotic cell contains a variety of structures, however, all the structures are not found in every prokaryotic organism, A prokaryotic cell is bounded by a chemically complex cell wall. A cell membrane lies below the cell wall and surrounds the inner cytoplasmic matrix. This cytoplasmic matrix include unbounded nucleoid, ribosomes and some inclusion bodies. External to the cell wall there occurs extra components possessing different functions. The most typical example for prokaryotic cell organization is the bacterial cell. Structurally a bacterial cell consists of Structures external to the cell wall, cell wall and structures internal to the cell wall.
Microorganisms exist as either prokaryotes or eukaryotes. The prokaryotic cells are morphologically much simpler than eukaryotic cells. The prokaryotic cells lack internal membrane bound organelles that are present in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells such as mitochondria and chloroplast etc. Though simple, prokaryotic cell contains a variety of structures, however, all the structures are not found in every prokaryotic organism, A prokaryotic cell is bounded by a chemically complex cell wall. A cell membrane lies below the cell wall and surrounds the inner cytoplasmic matrix. This cytoplasmic matrix include unbounded nucleoid, ribosomes and some inclusion bodies. External to the cell wall there occurs extra components possessing different functions. The most typical example for prokaryotic cell organization is the bacterial cell. Structurally a bacterial cell consists of Structures external to the cell wall, cell wall and structures internal to the cell wall.
0
 Virus literally means ‘poison’. They are also called as filterable molecules during olden days as they are able to pass through filter pores which do not permit bacteria to pass. They are the submicroscopic entities. Andre Luoff, a virologist and Nobel Laureate, defined the viruses as “Viruses are Viruses”.
Virus literally means ‘poison’. They are also called as filterable molecules during olden days as they are able to pass through filter pores which do not permit bacteria to pass. They are the submicroscopic entities. Andre Luoff, a virologist and Nobel Laureate, defined the viruses as “Viruses are Viruses”.
The general characteristics of Viruses are :
1. Viruses are a cellular organisms that are infectious in nature.
2. They are 10 to 100 times smaller than most bacteria and range from 20 to 200nm size.
3. They exist in two states namely extra cellular and intracellular.
4. They are obligate intracellular parasites
5. Viruses are incapable of independent growth in artificial media. They lack metabolic machinery of their own to generate energy or to synthesize proteins. Viruses depend on host cell machinery to carry out vital metabolic functions. However, they consist some genetic information for reproduction.
6. They reproduce only in living host cells such as plants, animals and microorganisms.
7. They structurally complete nature and infectious virus is called viron.
8. They possess either DNA or RNA as genetic material but never both.
9. The nucleic acid can be either single stranded or double stranded.
10. Genetic material is enclosed in a highly specialized protein coat called capsid.
11. The capsid may be naked or enveloped.
12. Some viruses such as bacteriophases possess a banal structure of head and tail attached.
13. They are neither prokaryotic or eukaryotic. They do not consist cytoplasm and cytoplasmic organelles.
14. Several viruses cause different diseases in plants, animals and human beings.
Leia Mais
VIRUS
 Virus literally means ‘poison’. They are also called as filterable molecules during olden days as they are able to pass through filter pores which do not permit bacteria to pass. They are the submicroscopic entities. Andre Luoff, a virologist and Nobel Laureate, defined the viruses as “Viruses are Viruses”.
Virus literally means ‘poison’. They are also called as filterable molecules during olden days as they are able to pass through filter pores which do not permit bacteria to pass. They are the submicroscopic entities. Andre Luoff, a virologist and Nobel Laureate, defined the viruses as “Viruses are Viruses”.The general characteristics of Viruses are :
1. Viruses are a cellular organisms that are infectious in nature.
2. They are 10 to 100 times smaller than most bacteria and range from 20 to 200nm size.
3. They exist in two states namely extra cellular and intracellular.
4. They are obligate intracellular parasites
5. Viruses are incapable of independent growth in artificial media. They lack metabolic machinery of their own to generate energy or to synthesize proteins. Viruses depend on host cell machinery to carry out vital metabolic functions. However, they consist some genetic information for reproduction.
6. They reproduce only in living host cells such as plants, animals and microorganisms.
7. They structurally complete nature and infectious virus is called viron.
8. They possess either DNA or RNA as genetic material but never both.
9. The nucleic acid can be either single stranded or double stranded.
10. Genetic material is enclosed in a highly specialized protein coat called capsid.
11. The capsid may be naked or enveloped.
12. Some viruses such as bacteriophases possess a banal structure of head and tail attached.
13. They are neither prokaryotic or eukaryotic. They do not consist cytoplasm and cytoplasmic organelles.
14. Several viruses cause different diseases in plants, animals and human beings.
0

In bacteria sexual reproduction is of three types :
Transformation : The process of uptake of a complete or fragment of a naked DNA molecule by a competent cell from the medium and incorporation of this molecule into recipient chromosome in a heritable form is called as transformation. This type of gene transfer is discovered and demonstrated by Fred Griffith. The process of transformation is random and any portion of a genome may be transferred between bacteria. The process of transformation is an important and natural route of genetic exchange in bacteria. The transformation, as natural phenomenon, is found only in certain gram +ve and gram –ve bacteria such as Streptococcus, Bacillus, Thermoactinomyces Haemophilus, Azotobacter, Pseudomonas etc. In laboratories, the transformation is carried out artificially by treating the cells with calcium chloride. This treatment makes the cell membrane more permeable to DNA. However, the frequency of the transformation increases with high concentration of DNA.
Conjugation : The process of transfer of genetic material from one cell to another cell through direct cell-cell contact is called as conjugation. This process of conjugation was discovered in E.coli by J.Lederberg and E.L. Tatum in 1976. Later, scientists namely Hayes, Jacols and wollman proved that gene transfer in this process occurs only in one direction and it is non- reciprocal. This one-way gene transfer takes place from male or donor cell to female or recipient cell. Normally much longer DNA fragment is transferred in this conjugation process when compared to that of transformation process. Besides the main chromosome, some of the bacterial cells contain one or more. Small DNA molecules called as plasmids. This extra chromosomal genetic material can also be transferred from one cell to another cell through conjugation process.
Transduction : Transduction is defined as a process of genetic transfer from donor bacterial cell to recipient bacterial cell mediated through a bacteriophage. This process is first discovered by Norton Zinder and Joshua Lederberg in Salmonella, by a variety of bacteriophages. Transduction is one of the most common mechanism for gene exchange and recombination in bacteria. There are two type of transduction processes namely generalized transduction and specialized transduction.
Leia Mais
SEXUAL REPORDUCTION IN BACTERIA

In bacteria sexual reproduction is of three types :
Transformation : The process of uptake of a complete or fragment of a naked DNA molecule by a competent cell from the medium and incorporation of this molecule into recipient chromosome in a heritable form is called as transformation. This type of gene transfer is discovered and demonstrated by Fred Griffith. The process of transformation is random and any portion of a genome may be transferred between bacteria. The process of transformation is an important and natural route of genetic exchange in bacteria. The transformation, as natural phenomenon, is found only in certain gram +ve and gram –ve bacteria such as Streptococcus, Bacillus, Thermoactinomyces Haemophilus, Azotobacter, Pseudomonas etc. In laboratories, the transformation is carried out artificially by treating the cells with calcium chloride. This treatment makes the cell membrane more permeable to DNA. However, the frequency of the transformation increases with high concentration of DNA.
Conjugation : The process of transfer of genetic material from one cell to another cell through direct cell-cell contact is called as conjugation. This process of conjugation was discovered in E.coli by J.Lederberg and E.L. Tatum in 1976. Later, scientists namely Hayes, Jacols and wollman proved that gene transfer in this process occurs only in one direction and it is non- reciprocal. This one-way gene transfer takes place from male or donor cell to female or recipient cell. Normally much longer DNA fragment is transferred in this conjugation process when compared to that of transformation process. Besides the main chromosome, some of the bacterial cells contain one or more. Small DNA molecules called as plasmids. This extra chromosomal genetic material can also be transferred from one cell to another cell through conjugation process.
Transduction : Transduction is defined as a process of genetic transfer from donor bacterial cell to recipient bacterial cell mediated through a bacteriophage. This process is first discovered by Norton Zinder and Joshua Lederberg in Salmonella, by a variety of bacteriophages. Transduction is one of the most common mechanism for gene exchange and recombination in bacteria. There are two type of transduction processes namely generalized transduction and specialized transduction.
0
 Some organisms are very small and can’t be seen with the unaided human eye. Hence these small and invisible organisms is called MICROBIOLOGY.
Some organisms are very small and can’t be seen with the unaided human eye. Hence these small and invisible organisms is called MICROBIOLOGY.
Organism with a diameter of 1mm or less are can’t be seen with the human eye. Hence these organisms are called after the invention of microscope. Traditionally microorganism had been included in Botany or Zoology. The present day biologists can’t agree with the inclusion of these microorganisms in Botany or Zoology because they exhibit greater diversity than plants or animals.
Classification of Microorganisms:
At present five groups of organisms are identified in micro organisms.
1. Bacteria
2. Viruses
3. Algae
4. Fungi
5. Protozoa.
Hence Microbiology has been classified into five branches.
(1) Viruses : These are acellular, infectious agents. They have no living characters except replication, Nuclic acid. They cause several diseases.
(2) Bacteria : these are smallest unicellular organisms. They show prokaryotic cellular organization. Ex : Eubacteria, Cynobacteria, Mycoplasmas, Rickettsiae and Chlamydiae
(3) Algae : these are plgmented, photosynthetic autotrophic micro organisms. Ex : Chylamydomonas, Spirogyra etc.
(4) Fungi : these are heterotrophic, non-green, eukarotic microorganisms. They posses a thick wall usually made up of polysaccharides (chitin). The body is made up of filaments called hyphae with forms into a mycelium. Ex : Pencillium, Puccinia, Mucor, Agaricus etc.
(5) Protozoa : These are commonly defined as unicellular, eukaryotic, non- photosynthetic microorganisms. Ex : Amoeba, Plasmodium, Paramecium.
Leia Mais
IMPORTANCE AND SCOPE OF MICROBIOLOGY AS A MODERN SCIENCE
 Some organisms are very small and can’t be seen with the unaided human eye. Hence these small and invisible organisms is called MICROBIOLOGY.
Some organisms are very small and can’t be seen with the unaided human eye. Hence these small and invisible organisms is called MICROBIOLOGY.Organism with a diameter of 1mm or less are can’t be seen with the human eye. Hence these organisms are called after the invention of microscope. Traditionally microorganism had been included in Botany or Zoology. The present day biologists can’t agree with the inclusion of these microorganisms in Botany or Zoology because they exhibit greater diversity than plants or animals.
Classification of Microorganisms:
At present five groups of organisms are identified in micro organisms.
1. Bacteria
2. Viruses
3. Algae
4. Fungi
5. Protozoa.
Hence Microbiology has been classified into five branches.
(1) Viruses : These are acellular, infectious agents. They have no living characters except replication, Nuclic acid. They cause several diseases.
(2) Bacteria : these are smallest unicellular organisms. They show prokaryotic cellular organization. Ex : Eubacteria, Cynobacteria, Mycoplasmas, Rickettsiae and Chlamydiae
(3) Algae : these are plgmented, photosynthetic autotrophic micro organisms. Ex : Chylamydomonas, Spirogyra etc.
(4) Fungi : these are heterotrophic, non-green, eukarotic microorganisms. They posses a thick wall usually made up of polysaccharides (chitin). The body is made up of filaments called hyphae with forms into a mycelium. Ex : Pencillium, Puccinia, Mucor, Agaricus etc.
(5) Protozoa : These are commonly defined as unicellular, eukaryotic, non- photosynthetic microorganisms. Ex : Amoeba, Plasmodium, Paramecium.
0
 Microorganisms are widespread and omnipresent. They live in water, air and soil. They also live in side the plants and animals. Microorganisms are widely employed in many industries connected with the manufacture of food, medicines, textiles and chemicals. They improve soil fertility. Microorganisms are also associated with the health and welfare of human beings. Microorganisms like viruses, bacteria and fungi cause several diseases in animals, human beings and plants. The spoilage of food materials, industrial substances, wood, iron pipes is also due to the action of microorganisms.
Leia Mais
Microorganisms are widespread and omnipresent. They live in water, air and soil. They also live in side the plants and animals. Microorganisms are widely employed in many industries connected with the manufacture of food, medicines, textiles and chemicals. They improve soil fertility. Microorganisms are also associated with the health and welfare of human beings. Microorganisms like viruses, bacteria and fungi cause several diseases in animals, human beings and plants. The spoilage of food materials, industrial substances, wood, iron pipes is also due to the action of microorganisms.
Leia Mais
MICROBES AND THEIR DISTRIBUTION
 Microorganisms are widespread and omnipresent. They live in water, air and soil. They also live in side the plants and animals. Microorganisms are widely employed in many industries connected with the manufacture of food, medicines, textiles and chemicals. They improve soil fertility. Microorganisms are also associated with the health and welfare of human beings. Microorganisms like viruses, bacteria and fungi cause several diseases in animals, human beings and plants. The spoilage of food materials, industrial substances, wood, iron pipes is also due to the action of microorganisms.
Microorganisms are widespread and omnipresent. They live in water, air and soil. They also live in side the plants and animals. Microorganisms are widely employed in many industries connected with the manufacture of food, medicines, textiles and chemicals. They improve soil fertility. Microorganisms are also associated with the health and welfare of human beings. Microorganisms like viruses, bacteria and fungi cause several diseases in animals, human beings and plants. The spoilage of food materials, industrial substances, wood, iron pipes is also due to the action of microorganisms.
0
 Microorganisms serve as specific agents for large scale chemical transformations, specially variety of geochemical changes. Winogradsky and Beijerink proved that microbes play important role in the Carbon cycle, Nitrogen cycle, Sulphur cycle etc. they also proved the role of microorganism in the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen fixation.
Microorganisms serve as specific agents for large scale chemical transformations, specially variety of geochemical changes. Winogradsky and Beijerink proved that microbes play important role in the Carbon cycle, Nitrogen cycle, Sulphur cycle etc. they also proved the role of microorganism in the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen fixation.
Microbiology contributed significantly to the development of new branches like biochemistry and Genetics. Buchner discovered cell- free alcoholic fermentation which became a foundation to the biochemistry. The studies on microorganisms helped in the discovery of vitamins, enzyme.
Beadle and Tatum isolated a series of biochemical mutants from fungus called Neurospora. Delbruck and luria carried researches on mutation in bacteria. Several mechanisms of genetic transfer were discovered in bacteria (conjugation, transduction, transformation).
Avery Mc Leod and Mc cart basing on the studies of genetic transformation studies in bacteria discovered that genetic matter in living organisms is DNA.
Microbiology made many contributions for the development of molecular biology.
Microorganisms are responsible for the manufacture of various foods of man. The biochemical reactions of microorganism helps in the process of production of foods like Curd, Bread, Alochol, Soya Souce, SCP protein etc. the fruiting bodies of some fungi like Agaricus, Plurotus etc are used as mushrooms, SCP protein are synthesized from culturing of micro organisms like Chlorella, Spirulina, Yeasts etc.
Microorganisms helps in several industries like medicine industry, jute industry. Hormones, Vitamins, Vaccins are also manufactured from microorganisms. They also used in Recombinant technology, cell fusion technology etc.
Hence the branch microbiology developed into a independent modern branch of science.
Leia Mais
IMPORTANCE OF MICROBIOLOGY
 Microorganisms serve as specific agents for large scale chemical transformations, specially variety of geochemical changes. Winogradsky and Beijerink proved that microbes play important role in the Carbon cycle, Nitrogen cycle, Sulphur cycle etc. they also proved the role of microorganism in the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen fixation.
Microorganisms serve as specific agents for large scale chemical transformations, specially variety of geochemical changes. Winogradsky and Beijerink proved that microbes play important role in the Carbon cycle, Nitrogen cycle, Sulphur cycle etc. they also proved the role of microorganism in the fixation of atmospheric nitrogen fixation.Microbiology contributed significantly to the development of new branches like biochemistry and Genetics. Buchner discovered cell- free alcoholic fermentation which became a foundation to the biochemistry. The studies on microorganisms helped in the discovery of vitamins, enzyme.
Beadle and Tatum isolated a series of biochemical mutants from fungus called Neurospora. Delbruck and luria carried researches on mutation in bacteria. Several mechanisms of genetic transfer were discovered in bacteria (conjugation, transduction, transformation).
Avery Mc Leod and Mc cart basing on the studies of genetic transformation studies in bacteria discovered that genetic matter in living organisms is DNA.
Microbiology made many contributions for the development of molecular biology.
Microorganisms are responsible for the manufacture of various foods of man. The biochemical reactions of microorganism helps in the process of production of foods like Curd, Bread, Alochol, Soya Souce, SCP protein etc. the fruiting bodies of some fungi like Agaricus, Plurotus etc are used as mushrooms, SCP protein are synthesized from culturing of micro organisms like Chlorella, Spirulina, Yeasts etc.
Microorganisms helps in several industries like medicine industry, jute industry. Hormones, Vitamins, Vaccins are also manufactured from microorganisms. They also used in Recombinant technology, cell fusion technology etc.
Hence the branch microbiology developed into a independent modern branch of science.
0

The first person who discovered microorganism was a Dutch merchant Anton Van Leeuwenhoek. He named them as animalcules or little animals. Later scientific experiments helped to disprove the theory of spontaneous generation. Lewis Pasteur stated that microorganisms bring about chemical changes in organic infusions. The disease ‘late blight of potato’ which is responsible for Irish famine was due to fungus. Berkely identified that the disease causing organism of ‘late blight of potato’ is fungus. Brigerinck isolated nitrogen fixing bacteria like Azatobacter and Rhizobium. Winogradsky isolated sulpur and Iron bacteria.
The first antibiotic penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming. This antibiotic is produced by a fungus called pernicillium notatum. Waksman discovered the antibiotic called streptomycin from bacteria. Lederberg and Tatum discovered a type of sexual reproduction called conjugation in bacteria. Watson & Crick proposed a model for the structure of DNA which is called as ‘Double helical structure. Jacob and Monod proposed Operon Concept’ for explaining gene concept. Diener discovered viroids. Nerenberg and Koran proposed genetic code triplet code.
Leia Mais
HISTORY OF MICROBIOLOGY

The first person who discovered microorganism was a Dutch merchant Anton Van Leeuwenhoek. He named them as animalcules or little animals. Later scientific experiments helped to disprove the theory of spontaneous generation. Lewis Pasteur stated that microorganisms bring about chemical changes in organic infusions. The disease ‘late blight of potato’ which is responsible for Irish famine was due to fungus. Berkely identified that the disease causing organism of ‘late blight of potato’ is fungus. Brigerinck isolated nitrogen fixing bacteria like Azatobacter and Rhizobium. Winogradsky isolated sulpur and Iron bacteria.
The first antibiotic penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming. This antibiotic is produced by a fungus called pernicillium notatum. Waksman discovered the antibiotic called streptomycin from bacteria. Lederberg and Tatum discovered a type of sexual reproduction called conjugation in bacteria. Watson & Crick proposed a model for the structure of DNA which is called as ‘Double helical structure. Jacob and Monod proposed Operon Concept’ for explaining gene concept. Diener discovered viroids. Nerenberg and Koran proposed genetic code triplet code.
0
 Refers to any heritable change in nucleotide sequence of a gene of the organisms irrespective of altered phenotypic expression of characters of the organisms. A gene codes for a protein, therefore, the physical and chemical properties of proteins are changed due to alteration in genes. Genes are made up of nucleotide sequences. Hence, changes in a gene refer to changes in nucleotide or nucleotide sequence. For example, if the normal sequence was ATT, the change to AAT may lead to entirely different amino acids into a polypeptide chain. Therefore, mutation is the result of stable and heritable changes in nucleotide sequence of DNA. These changes may include alteration of a single base pair of nucleotides or addition/deletion of one or more nucleotides in the coding region of a gene.
Refers to any heritable change in nucleotide sequence of a gene of the organisms irrespective of altered phenotypic expression of characters of the organisms. A gene codes for a protein, therefore, the physical and chemical properties of proteins are changed due to alteration in genes. Genes are made up of nucleotide sequences. Hence, changes in a gene refer to changes in nucleotide or nucleotide sequence. For example, if the normal sequence was ATT, the change to AAT may lead to entirely different amino acids into a polypeptide chain. Therefore, mutation is the result of stable and heritable changes in nucleotide sequence of DNA. These changes may include alteration of a single base pair of nucleotides or addition/deletion of one or more nucleotides in the coding region of a gene.
When an amino acid substitution has no detectable effect on phenotype, it is known as silent mutation. On the other hand if a bacterium carries such a mutation in the enzyme that synthesizes an essential amino acid, it can grow very slowly unless the medium is supplied with that substance. This type of mutation is called leaky mutation.
For an organism to exist with stability, it is necessary that the nucleotide sequence of its gene must not be altered to such an extent that can promote instability. Changes to some extent brings about alteration in phenotypic expression. Though changes in genetic make up is harmful to an organism, but it is necessary to generate variability in organism and contribute to the process of evolution in nature.
The process of formation of a mutant organism is known as mutagenesis. Mutagenesis occurs in an organism by two mechanisms, (i) spontaneously (ii) through physical or chemical agents. The mutation that arises all of sudden without any effort is called spontaneous mutation. The mutation that arises through induction by addition of chemicals (i.e. mutagens) or radiation is called induced mutation.
Leia Mais
MUTATION AND MUTAGENESIS
 Refers to any heritable change in nucleotide sequence of a gene of the organisms irrespective of altered phenotypic expression of characters of the organisms. A gene codes for a protein, therefore, the physical and chemical properties of proteins are changed due to alteration in genes. Genes are made up of nucleotide sequences. Hence, changes in a gene refer to changes in nucleotide or nucleotide sequence. For example, if the normal sequence was ATT, the change to AAT may lead to entirely different amino acids into a polypeptide chain. Therefore, mutation is the result of stable and heritable changes in nucleotide sequence of DNA. These changes may include alteration of a single base pair of nucleotides or addition/deletion of one or more nucleotides in the coding region of a gene.
Refers to any heritable change in nucleotide sequence of a gene of the organisms irrespective of altered phenotypic expression of characters of the organisms. A gene codes for a protein, therefore, the physical and chemical properties of proteins are changed due to alteration in genes. Genes are made up of nucleotide sequences. Hence, changes in a gene refer to changes in nucleotide or nucleotide sequence. For example, if the normal sequence was ATT, the change to AAT may lead to entirely different amino acids into a polypeptide chain. Therefore, mutation is the result of stable and heritable changes in nucleotide sequence of DNA. These changes may include alteration of a single base pair of nucleotides or addition/deletion of one or more nucleotides in the coding region of a gene.When an amino acid substitution has no detectable effect on phenotype, it is known as silent mutation. On the other hand if a bacterium carries such a mutation in the enzyme that synthesizes an essential amino acid, it can grow very slowly unless the medium is supplied with that substance. This type of mutation is called leaky mutation.
For an organism to exist with stability, it is necessary that the nucleotide sequence of its gene must not be altered to such an extent that can promote instability. Changes to some extent brings about alteration in phenotypic expression. Though changes in genetic make up is harmful to an organism, but it is necessary to generate variability in organism and contribute to the process of evolution in nature.
The process of formation of a mutant organism is known as mutagenesis. Mutagenesis occurs in an organism by two mechanisms, (i) spontaneously (ii) through physical or chemical agents. The mutation that arises all of sudden without any effort is called spontaneous mutation. The mutation that arises through induction by addition of chemicals (i.e. mutagens) or radiation is called induced mutation.
0
 The genes of transposase and resolvase i.e. tnpR and tnpR are identified by recessive mutations. The above enzymes accomplish the two stages of TnA mediated transposition. Like IS- type elements the transposition stage involves the ends of the elements. A unique feature of TnA family is that a specific internal site is required for resolution.
The genes of transposase and resolvase i.e. tnpR and tnpR are identified by recessive mutations. The above enzymes accomplish the two stages of TnA mediated transposition. Like IS- type elements the transposition stage involves the ends of the elements. A unique feature of TnA family is that a specific internal site is required for resolution.
The mutants of tnpA cannot transpose because the enzyme transposase will not be encoded. However, transposase recognizes the ends of elements and binds to 25 bp long sequence located within 38 bp of the inverted terminal repeat. Transposase also makes the staggered 5 bp long sequence breaks in target DNA where transposon is to be inserted. Resolvase functions in two ways, (i) it acts as repressor of gene expressions, and (ii) provide the resolvase function. The frequency of transposition gets increased in tnpR mutants because tnpR represses the transcription of both tnpA and its own gene. Inactivation of tnpR protein allows the increased synthesis of tnpA resulting in the increased transposition frequency. Therefore, the amount of tnpA transposase is a limiting factor in transposition.
The genes, tnpA and tnpR express divergently from an ATP rich enter-cistronic central region. The effects of tnpR are also medicated by its binding in this region. TnpR resolvase gets involved in recombination between direct repeats of Tn3 in a co integrate structure. But in Tn3, resolution reaction occurs only at a specific site.
The res is the site where the recombination carried by tnpR resolvase occurs. The res site is identified by cis-acting deletions. The deletions block transposition resulting in accumulation of co integrates. The sites bound by tnpR resolvase have been determined by foot printing the DNA- protein complex. It binds independently at each of three sites i.e. I, II and III, each 30-40 bp long. Site I is the region genetically defined as the res site. In the absence of site I, resolution reaction does not proceed. However, resolution also involves binding at sites II and III. In the absence of either of II and III sites reaction proceeds poorly. Site I overlaps with the start point for tnpA transcription and site II with the start point for tnpR transcription.
Leia Mais
GENETICS OF TRANSPOSITION
 The genes of transposase and resolvase i.e. tnpR and tnpR are identified by recessive mutations. The above enzymes accomplish the two stages of TnA mediated transposition. Like IS- type elements the transposition stage involves the ends of the elements. A unique feature of TnA family is that a specific internal site is required for resolution.
The genes of transposase and resolvase i.e. tnpR and tnpR are identified by recessive mutations. The above enzymes accomplish the two stages of TnA mediated transposition. Like IS- type elements the transposition stage involves the ends of the elements. A unique feature of TnA family is that a specific internal site is required for resolution.The mutants of tnpA cannot transpose because the enzyme transposase will not be encoded. However, transposase recognizes the ends of elements and binds to 25 bp long sequence located within 38 bp of the inverted terminal repeat. Transposase also makes the staggered 5 bp long sequence breaks in target DNA where transposon is to be inserted. Resolvase functions in two ways, (i) it acts as repressor of gene expressions, and (ii) provide the resolvase function. The frequency of transposition gets increased in tnpR mutants because tnpR represses the transcription of both tnpA and its own gene. Inactivation of tnpR protein allows the increased synthesis of tnpA resulting in the increased transposition frequency. Therefore, the amount of tnpA transposase is a limiting factor in transposition.
The genes, tnpA and tnpR express divergently from an ATP rich enter-cistronic central region. The effects of tnpR are also medicated by its binding in this region. TnpR resolvase gets involved in recombination between direct repeats of Tn3 in a co integrate structure. But in Tn3, resolution reaction occurs only at a specific site.
The res is the site where the recombination carried by tnpR resolvase occurs. The res site is identified by cis-acting deletions. The deletions block transposition resulting in accumulation of co integrates. The sites bound by tnpR resolvase have been determined by foot printing the DNA- protein complex. It binds independently at each of three sites i.e. I, II and III, each 30-40 bp long. Site I is the region genetically defined as the res site. In the absence of site I, resolution reaction does not proceed. However, resolution also involves binding at sites II and III. In the absence of either of II and III sites reaction proceeds poorly. Site I overlaps with the start point for tnpA transcription and site II with the start point for tnpR transcription.
0

The transfer of genetic material from one cell to another by a bacteriophage is called transduction. The phenomenon of transduction was first discovered by Zinder and Lederberg while searching for sexual conjugation in Salmonella species.
The infection by a bacteriophage is accomplished in several stages such as adsorption, penetration, replication, assembly, lysis and release. In brief the virus particles first attaches to specific receptor site on bacterial call wall surface. The genetic material penetrates the bacterial call, and replicates independently by using cell machinery of the host. Consequently, the virus DNA is replicated into multiple copies, and synthesizes phage proteins. Complete phage particles are assembled and finally cell is lysed resulting in release of virus particles.
Depending on mode of reproduction that reproduction the bacteriophages are of two types, the virulent phage and the temperate phage, the phage that reproduce by using a lytic cycle are called virulent phages because they destroy the host cell such as T phage, phage lambda, etc. in contrast the temperate phages ordinarily, do not lyse the bacterial cell. The viral genome behaves as episome like F factor and becomes integrated into the bacterial chromosome. The latent form of phage genome that remains within the host without harm and integrates with chromosome is called prophage. Bacteria containing prophage are known as lysogenic bacteria and the relationship between phage and its host is called lysogeny. The lysogenic bacteria can produce phage particles under some conditions, and the phage is able to establish the phenomenon of lysogeny and behaves as temperate phage.
Usually, transduction occurs most readily between the closely related species of same genus of a bacterium i.e. intrageneric. This preference is due requirement for specific cell surface receptor for recognition of the phage. In addition, intergeneric transduction has been shown between the closely related enteric bacteria such as between E. coli salmonella or shigella species. Several genetic traits for example fermentation potential, antigens, chemical resistance are transducible.
Leia Mais
TRANSDUCTION

The transfer of genetic material from one cell to another by a bacteriophage is called transduction. The phenomenon of transduction was first discovered by Zinder and Lederberg while searching for sexual conjugation in Salmonella species.
The infection by a bacteriophage is accomplished in several stages such as adsorption, penetration, replication, assembly, lysis and release. In brief the virus particles first attaches to specific receptor site on bacterial call wall surface. The genetic material penetrates the bacterial call, and replicates independently by using cell machinery of the host. Consequently, the virus DNA is replicated into multiple copies, and synthesizes phage proteins. Complete phage particles are assembled and finally cell is lysed resulting in release of virus particles.
Depending on mode of reproduction that reproduction the bacteriophages are of two types, the virulent phage and the temperate phage, the phage that reproduce by using a lytic cycle are called virulent phages because they destroy the host cell such as T phage, phage lambda, etc. in contrast the temperate phages ordinarily, do not lyse the bacterial cell. The viral genome behaves as episome like F factor and becomes integrated into the bacterial chromosome. The latent form of phage genome that remains within the host without harm and integrates with chromosome is called prophage. Bacteria containing prophage are known as lysogenic bacteria and the relationship between phage and its host is called lysogeny. The lysogenic bacteria can produce phage particles under some conditions, and the phage is able to establish the phenomenon of lysogeny and behaves as temperate phage.
Usually, transduction occurs most readily between the closely related species of same genus of a bacterium i.e. intrageneric. This preference is due requirement for specific cell surface receptor for recognition of the phage. In addition, intergeneric transduction has been shown between the closely related enteric bacteria such as between E. coli salmonella or shigella species. Several genetic traits for example fermentation potential, antigens, chemical resistance are transducible.
0
GENETIC NOTATION
If a bacterial cell synthesizes amino acid leucine, it is represented as Leu+, and if it does not it is denoted as Leu+. The symbol has capitalized (not italicized) the letters. It denotes that Leu- has some defective genes which cripple the cell to synthesize leucine. The defective gene is represented as leu- (italicized three letters). However, if more than one gene are needed to synthesize leucine, it is denoted as leuA, leuB, etc. and the functional gene as leuA+ leuB, etc.
It should be kept in mind that the bacteria always have a single set of genes i.e. they are haploid. The eukaryotic organisms are haploid as well as diploid but the dominance of these two phases in the life of an organism differs. The diploid cells of organisms contain two sets of genes. The double sets of functional genes are represented as leu+/leu. They may have normal or defective gones. The functional form of a gene is called wild type.
However, if a bacterium is resistant to certain antibiotics it is represented by giving the symbols, for example Tet (resistant to tetracycline), Amp (resistant to ampicillin), Kan (resistant to Kanamycin), etc. the microorganisms susceptible to the above antibiotics are represented as Tet, Amp, Kan, etc.
Mutations occurring in genotype are also represented by numbers in the order in which they have been isolated. For example, if leucine mutation has occurred on 58 and 79 position it is written as leu58 and leu79 respectively. More specifically to denote the mutation on a particular gene e.g. A and B, it is written as leuA58 and leuB79 if mutation has occurred in leuA and leuB genes, respectively.
Leia Mais
It should be kept in mind that the bacteria always have a single set of genes i.e. they are haploid. The eukaryotic organisms are haploid as well as diploid but the dominance of these two phases in the life of an organism differs. The diploid cells of organisms contain two sets of genes. The double sets of functional genes are represented as leu+/leu. They may have normal or defective gones. The functional form of a gene is called wild type.
However, if a bacterium is resistant to certain antibiotics it is represented by giving the symbols, for example Tet (resistant to tetracycline), Amp (resistant to ampicillin), Kan (resistant to Kanamycin), etc. the microorganisms susceptible to the above antibiotics are represented as Tet, Amp, Kan, etc.
Mutations occurring in genotype are also represented by numbers in the order in which they have been isolated. For example, if leucine mutation has occurred on 58 and 79 position it is written as leu58 and leu79 respectively. More specifically to denote the mutation on a particular gene e.g. A and B, it is written as leuA58 and leuB79 if mutation has occurred in leuA and leuB genes, respectively.
0
ORIGIN AND EVOLUTION OF GENETIC CODE
From the discussion of genetic code some important facts came into light as the degeneracy and universality of the genetic code. It may be supposed that present from of genetic code would have evolved from a more primitive code which must have occurred about three billion years ago. Since the evolution of bacteria, the code has remained fixed. Any mutation that altered the sequence would changed the reading frame of mRNA resulting in changes in specifying amino acids. Wong has discussed in detail about the evolution of genetic code
Leia Mais
0
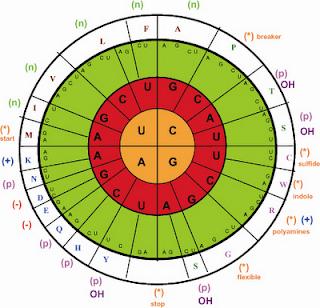 Genetic code is universal and does not undergo any change. But during 1980s, it was discovered that the genetic code of mitochondria of yeasts, Drosophila and mammals differs from the universal genetic code. The mitochondrial genome is usually circular DNA molecule and contains complete genetic system. Anderson et al for the first time through DNA sequencing technique presented the complete sequence of 16,569 nuclear, of human mitochondrial genome. The human mitochondrial genome differs from that of nuclear, chloroplast and bacterial genome in the following respect:
Genetic code is universal and does not undergo any change. But during 1980s, it was discovered that the genetic code of mitochondria of yeasts, Drosophila and mammals differs from the universal genetic code. The mitochondrial genome is usually circular DNA molecule and contains complete genetic system. Anderson et al for the first time through DNA sequencing technique presented the complete sequence of 16,569 nuclear, of human mitochondrial genome. The human mitochondrial genome differs from that of nuclear, chloroplast and bacterial genome in the following respect:
(i) Unlike others, every nucleotide appears to be a part of coding sequence.
(ii) The normal codon-anticodon pairing rules are relaxed in mitochondria, therefore, many there are 22 t RNAs in mitochondria and about 55 t RNAs in universal code.
(iii) The genetic code is different from those of the same codons in other genomes. However, the genetic code of mitochondria differs from the universal genetic code on the other hand the mitochondrial genetic code in different group of organisms also differ. For example, UGA which is a stop codon elsewhere is read as tryptophan in mitochondria of yeasts, Drosophila, mammals and protozoa, but as stop codon in mitochondria. The codon AGG normally codes for arginine, but it acts as stop codon in mitochondria of mammals, and codes for serine in Drosophila, UGA codon which codes for isoleusine, specifies methionine in yeasts, Drosophila and mammal’s mitochondria.
Leia Mais
GENETIC CODE IN MITOCHONDRIA
 Genetic code is universal and does not undergo any change. But during 1980s, it was discovered that the genetic code of mitochondria of yeasts, Drosophila and mammals differs from the universal genetic code. The mitochondrial genome is usually circular DNA molecule and contains complete genetic system. Anderson et al for the first time through DNA sequencing technique presented the complete sequence of 16,569 nuclear, of human mitochondrial genome. The human mitochondrial genome differs from that of nuclear, chloroplast and bacterial genome in the following respect:
Genetic code is universal and does not undergo any change. But during 1980s, it was discovered that the genetic code of mitochondria of yeasts, Drosophila and mammals differs from the universal genetic code. The mitochondrial genome is usually circular DNA molecule and contains complete genetic system. Anderson et al for the first time through DNA sequencing technique presented the complete sequence of 16,569 nuclear, of human mitochondrial genome. The human mitochondrial genome differs from that of nuclear, chloroplast and bacterial genome in the following respect:(i) Unlike others, every nucleotide appears to be a part of coding sequence.
(ii) The normal codon-anticodon pairing rules are relaxed in mitochondria, therefore, many there are 22 t RNAs in mitochondria and about 55 t RNAs in universal code.
(iii) The genetic code is different from those of the same codons in other genomes. However, the genetic code of mitochondria differs from the universal genetic code on the other hand the mitochondrial genetic code in different group of organisms also differ. For example, UGA which is a stop codon elsewhere is read as tryptophan in mitochondria of yeasts, Drosophila, mammals and protozoa, but as stop codon in mitochondria. The codon AGG normally codes for arginine, but it acts as stop codon in mitochondria of mammals, and codes for serine in Drosophila, UGA codon which codes for isoleusine, specifies methionine in yeasts, Drosophila and mammal’s mitochondria.
1
 Recently, fully automated commercial instrument called automated polynucleotide synthesizer gene machine is available in market which synthesizes predetermined polynucleotide sequence. Therefore, the gene can be synthesized rapidly and in high amount. For example, a gene for t RNA can be synthesized within a few days through gene machine. It automatically synthesizes of single stranded DNA under the control of microprocessor. The working principle of a gene machine includes (i) development of insoluble silica based support in the form of beads which provides support for solid phase synthesis of DNA chain, and (ii) development of stable deoxyribonucleoside phosphoramidites as synthons which are stable to oxidation and hydrolysis, and ideal for DNA synthesis.
Recently, fully automated commercial instrument called automated polynucleotide synthesizer gene machine is available in market which synthesizes predetermined polynucleotide sequence. Therefore, the gene can be synthesized rapidly and in high amount. For example, a gene for t RNA can be synthesized within a few days through gene machine. It automatically synthesizes of single stranded DNA under the control of microprocessor. The working principle of a gene machine includes (i) development of insoluble silica based support in the form of beads which provides support for solid phase synthesis of DNA chain, and (ii) development of stable deoxyribonucleoside phosphoramidites as synthons which are stable to oxidation and hydrolysis, and ideal for DNA synthesis.
The mechanism of a gene machine is four separate reservoirs containing nucleotides (A,T,C and G) are connected with a tube to a cylinder (synthesiser column) packed with small silica beads. These beads provide support for assembly of DNA molecules. Reservoirs for reagent and solvent are also attached. The whole procedure of adding or removing the chemicals from the reagent reservoir in time is controlled by microcomputer control system i.e. microprocessor.
If one desires to synthesize a short polynucleotide with a sequence of nucleotides T,G,C, the cylinder is first filled with beads with a single T attached. Thereafter, it is flooded with G from the reservoir. The right hand side of each G is blocked by using chemicals from the reservoir so that its attachment with any other Gs can be prevented. The remaining Gs which could not join with Ts are flushed from the cylinder. The other chemicals are passed from the reagent and solvent reservoirs so that these can remove the blocks from G which is attached with the T. In the same way this cycle is repeated by flooding with, C from reservoir into the cylinder. Finally the sequence T.G.C is synthesized on the silica beads which is removed chemically later on.
The desired sequence is entered on a key board and the microprocessor automatically opens the valve of nucleotide reservoir, and chemical and solvent reservoir. In the gene machine the nucleotides are added into a polynucleotide chain at the rate of two nucleotides per hour. By feeding the instructions of human insulin gene in gene machine insulin has been synthesized.
Leia Mais
GENE MACHINE
 Recently, fully automated commercial instrument called automated polynucleotide synthesizer gene machine is available in market which synthesizes predetermined polynucleotide sequence. Therefore, the gene can be synthesized rapidly and in high amount. For example, a gene for t RNA can be synthesized within a few days through gene machine. It automatically synthesizes of single stranded DNA under the control of microprocessor. The working principle of a gene machine includes (i) development of insoluble silica based support in the form of beads which provides support for solid phase synthesis of DNA chain, and (ii) development of stable deoxyribonucleoside phosphoramidites as synthons which are stable to oxidation and hydrolysis, and ideal for DNA synthesis.
Recently, fully automated commercial instrument called automated polynucleotide synthesizer gene machine is available in market which synthesizes predetermined polynucleotide sequence. Therefore, the gene can be synthesized rapidly and in high amount. For example, a gene for t RNA can be synthesized within a few days through gene machine. It automatically synthesizes of single stranded DNA under the control of microprocessor. The working principle of a gene machine includes (i) development of insoluble silica based support in the form of beads which provides support for solid phase synthesis of DNA chain, and (ii) development of stable deoxyribonucleoside phosphoramidites as synthons which are stable to oxidation and hydrolysis, and ideal for DNA synthesis.The mechanism of a gene machine is four separate reservoirs containing nucleotides (A,T,C and G) are connected with a tube to a cylinder (synthesiser column) packed with small silica beads. These beads provide support for assembly of DNA molecules. Reservoirs for reagent and solvent are also attached. The whole procedure of adding or removing the chemicals from the reagent reservoir in time is controlled by microcomputer control system i.e. microprocessor.
If one desires to synthesize a short polynucleotide with a sequence of nucleotides T,G,C, the cylinder is first filled with beads with a single T attached. Thereafter, it is flooded with G from the reservoir. The right hand side of each G is blocked by using chemicals from the reservoir so that its attachment with any other Gs can be prevented. The remaining Gs which could not join with Ts are flushed from the cylinder. The other chemicals are passed from the reagent and solvent reservoirs so that these can remove the blocks from G which is attached with the T. In the same way this cycle is repeated by flooding with, C from reservoir into the cylinder. Finally the sequence T.G.C is synthesized on the silica beads which is removed chemically later on.
The desired sequence is entered on a key board and the microprocessor automatically opens the valve of nucleotide reservoir, and chemical and solvent reservoir. In the gene machine the nucleotides are added into a polynucleotide chain at the rate of two nucleotides per hour. By feeding the instructions of human insulin gene in gene machine insulin has been synthesized.
0
 In 1975, Khorana and co-workers completed the synthesis of a gene for E.coli tyrosine
In 1975, Khorana and co-workers completed the synthesis of a gene for E.coli tyrosine
t RNA precursor. E.coli t RNA precursors are formed from the larger precursors. The tyrosine t RNA precursor has 126 nucleotides. They sunthyesized the complete sequence of DNA duplex coding for tyrosine –t RNA precursor of E.coli. though these segments are not the proper structural gene yet are the regions involved in its regulation.
Twenty six small oligonucleotide DNA segment giving rise to t RNA precursor was synthesized which were arranged into six double stranded fragments each containing single stranded ends. These six fragments were joined to give rise complete gene of 126 base pairs for tyrosine t RNA precursor of E. coli.
Khorana completely synthesized a biologically functional tyrosine t RNA suppressor gene of E.coli which was 207 base pairs long and contained (i) a 51 base pairs long DNA corresponding to promoter region, (ii) a 126 base pair long DNA corresponding to precursor region of t RNA, (iii) a 25 base pair long DNA including 16 base pairs contained restriction site for Eco RI. This complete synthetic gene was joined in phage lambda vector which in turn was allowed to transfect E.coli cells. After transfection phage containing synthetic gene successfully multiplied in E.coli.
Khorana made the phosphodiester approach for synthesizing the oligonucleotides of the biologically active t RNA. The demerits of this approach are: (i) the completion of reaction in long time, (ii) rapidly decrease in yield with the increase in chain length, and (iii) time taking procedure of purification.
Leia Mais
ARTIFICIAL SYNTHESIS OF A GENE FOR BACTERIAL TYROSINE tRNA
 In 1975, Khorana and co-workers completed the synthesis of a gene for E.coli tyrosine
In 1975, Khorana and co-workers completed the synthesis of a gene for E.coli tyrosinet RNA precursor. E.coli t RNA precursors are formed from the larger precursors. The tyrosine t RNA precursor has 126 nucleotides. They sunthyesized the complete sequence of DNA duplex coding for tyrosine –t RNA precursor of E.coli. though these segments are not the proper structural gene yet are the regions involved in its regulation.
Twenty six small oligonucleotide DNA segment giving rise to t RNA precursor was synthesized which were arranged into six double stranded fragments each containing single stranded ends. These six fragments were joined to give rise complete gene of 126 base pairs for tyrosine t RNA precursor of E. coli.
Khorana completely synthesized a biologically functional tyrosine t RNA suppressor gene of E.coli which was 207 base pairs long and contained (i) a 51 base pairs long DNA corresponding to promoter region, (ii) a 126 base pair long DNA corresponding to precursor region of t RNA, (iii) a 25 base pair long DNA including 16 base pairs contained restriction site for Eco RI. This complete synthetic gene was joined in phage lambda vector which in turn was allowed to transfect E.coli cells. After transfection phage containing synthetic gene successfully multiplied in E.coli.
Khorana made the phosphodiester approach for synthesizing the oligonucleotides of the biologically active t RNA. The demerits of this approach are: (i) the completion of reaction in long time, (ii) rapidly decrease in yield with the increase in chain length, and (iii) time taking procedure of purification.
0
 In 1940s, Beadle and Tatum proposed one-gene-one protein hypothesis which explains that one gene encodes for one protein. However, if one gene consists of 1,500 base pairs, a protein of 500 amino acids in length would be synthesized. In addition, if the same sequence read in two different ways, two different amino acids would be synthesized by the same sequence of base pairs. It means, the same DNA sequence can synthesize more than one proteins at different time. It was realized for the first time when the total number of proteins synthesized by X174 exceeded from the coding potential of the phage genome. A similar phonemenon is found in the tumour virus SV40 where the total molecular weight of proteins (i.e. VP1, VP2 and VP3) synthesized by SV40 genes is much more than the size of the DNA molecule (5200 base pairs i.e. 1,733 codons). From this observations the concept of overlapping genes has emerged.
Leia Mais
In 1940s, Beadle and Tatum proposed one-gene-one protein hypothesis which explains that one gene encodes for one protein. However, if one gene consists of 1,500 base pairs, a protein of 500 amino acids in length would be synthesized. In addition, if the same sequence read in two different ways, two different amino acids would be synthesized by the same sequence of base pairs. It means, the same DNA sequence can synthesize more than one proteins at different time. It was realized for the first time when the total number of proteins synthesized by X174 exceeded from the coding potential of the phage genome. A similar phonemenon is found in the tumour virus SV40 where the total molecular weight of proteins (i.e. VP1, VP2 and VP3) synthesized by SV40 genes is much more than the size of the DNA molecule (5200 base pairs i.e. 1,733 codons). From this observations the concept of overlapping genes has emerged.
Leia Mais
OVERLAPPING GENES (GENES WITHIN GENES)
 In 1940s, Beadle and Tatum proposed one-gene-one protein hypothesis which explains that one gene encodes for one protein. However, if one gene consists of 1,500 base pairs, a protein of 500 amino acids in length would be synthesized. In addition, if the same sequence read in two different ways, two different amino acids would be synthesized by the same sequence of base pairs. It means, the same DNA sequence can synthesize more than one proteins at different time. It was realized for the first time when the total number of proteins synthesized by X174 exceeded from the coding potential of the phage genome. A similar phonemenon is found in the tumour virus SV40 where the total molecular weight of proteins (i.e. VP1, VP2 and VP3) synthesized by SV40 genes is much more than the size of the DNA molecule (5200 base pairs i.e. 1,733 codons). From this observations the concept of overlapping genes has emerged.
In 1940s, Beadle and Tatum proposed one-gene-one protein hypothesis which explains that one gene encodes for one protein. However, if one gene consists of 1,500 base pairs, a protein of 500 amino acids in length would be synthesized. In addition, if the same sequence read in two different ways, two different amino acids would be synthesized by the same sequence of base pairs. It means, the same DNA sequence can synthesize more than one proteins at different time. It was realized for the first time when the total number of proteins synthesized by X174 exceeded from the coding potential of the phage genome. A similar phonemenon is found in the tumour virus SV40 where the total molecular weight of proteins (i.e. VP1, VP2 and VP3) synthesized by SV40 genes is much more than the size of the DNA molecule (5200 base pairs i.e. 1,733 codons). From this observations the concept of overlapping genes has emerged.
0

During 1970, in some mammalian viruses (e.g. adenoviruses) it was found that the DNA sequences coding for a polypeptide were not present continuously but were split into several pieces. Therefore, these genes were variously named as split genes or introns interrupted genes or interventing sequences inserts junk DNA. For the discovery of split genes in adenoviruses and higher organisms, Richards J.Roberts and Phillip sharp were awarded Nobel Prize in 1993.
We can see a DNA sequence codes for m RNA but the complete corresponding sequence of DNA is not found in m RNA. Certain sequences of DNA are missing in m RNA. The sequences present in DNA but missing in m RNA are called intervening sequences or introns, and the sequences of DNA found in RNA are known as exons. The exons code for m RNA.
Before the discovery of split genes in 1977, all the genes analysed in detail were the bacterial genes. Bacteria were considered to resemble the simpler cell from which eukaryotes must have been evolved. Now, it is supposed that split genes are the ancient condition and bacteria lost their introns only after evolution of most of their proteins. Evidence for the ancient origin of introns has been obtained by the examination of the gene that encodes the ubiquitous enzyme, triose phosphate isomerase (TPI). The TPI is coded by a gene that contains six introns (in vertebrates), five of these are present at the same position as in maize. The TPI play a key role in cell metabolism that catalyses the interconversion of glycolysis and glucogenesis. By comparing this enzyme in various organisms it appears that the TPI evolved before the divergence of prokaryotes and eukaryotes from a common ancestor cell-i.e. progenote (Nyberg and Cronhjort, 1992).
Leia Mais
SPLIT GENES

During 1970, in some mammalian viruses (e.g. adenoviruses) it was found that the DNA sequences coding for a polypeptide were not present continuously but were split into several pieces. Therefore, these genes were variously named as split genes or introns interrupted genes or interventing sequences inserts junk DNA. For the discovery of split genes in adenoviruses and higher organisms, Richards J.Roberts and Phillip sharp were awarded Nobel Prize in 1993.
We can see a DNA sequence codes for m RNA but the complete corresponding sequence of DNA is not found in m RNA. Certain sequences of DNA are missing in m RNA. The sequences present in DNA but missing in m RNA are called intervening sequences or introns, and the sequences of DNA found in RNA are known as exons. The exons code for m RNA.
Before the discovery of split genes in 1977, all the genes analysed in detail were the bacterial genes. Bacteria were considered to resemble the simpler cell from which eukaryotes must have been evolved. Now, it is supposed that split genes are the ancient condition and bacteria lost their introns only after evolution of most of their proteins. Evidence for the ancient origin of introns has been obtained by the examination of the gene that encodes the ubiquitous enzyme, triose phosphate isomerase (TPI). The TPI is coded by a gene that contains six introns (in vertebrates), five of these are present at the same position as in maize. The TPI play a key role in cell metabolism that catalyses the interconversion of glycolysis and glucogenesis. By comparing this enzyme in various organisms it appears that the TPI evolved before the divergence of prokaryotes and eukaryotes from a common ancestor cell-i.e. progenote (Nyberg and Cronhjort, 1992).
0
 There is genetic diversity among the microorganisms. The total number of genes in one microorganism differ from that in the other. For example, bacteriophage R17 and QB consist of only three genes. SV40 contains 5-10 genes. Ecoli consists about 4000 genes on about 1mm long chromosome. On the other hand the length of each gene varies in base composition. It may vary between 100 and 3000 nucleotides giving the complexity to proteins.
Leia Mais
There is genetic diversity among the microorganisms. The total number of genes in one microorganism differ from that in the other. For example, bacteriophage R17 and QB consist of only three genes. SV40 contains 5-10 genes. Ecoli consists about 4000 genes on about 1mm long chromosome. On the other hand the length of each gene varies in base composition. It may vary between 100 and 3000 nucleotides giving the complexity to proteins.
Leia Mais
GENETIC DIVERSITY
 There is genetic diversity among the microorganisms. The total number of genes in one microorganism differ from that in the other. For example, bacteriophage R17 and QB consist of only three genes. SV40 contains 5-10 genes. Ecoli consists about 4000 genes on about 1mm long chromosome. On the other hand the length of each gene varies in base composition. It may vary between 100 and 3000 nucleotides giving the complexity to proteins.
There is genetic diversity among the microorganisms. The total number of genes in one microorganism differ from that in the other. For example, bacteriophage R17 and QB consist of only three genes. SV40 contains 5-10 genes. Ecoli consists about 4000 genes on about 1mm long chromosome. On the other hand the length of each gene varies in base composition. It may vary between 100 and 3000 nucleotides giving the complexity to proteins.
0

one of the most important properties of DNA is that it forms its additional identical copies. The process of forming its replica copy is called replication.Replication is the basis of evolution of all morphologically complexed forms of life. Howard and Pelc demonstrated that in eukaryotes replication occurs during interphase between mitotic cycles and also during interphase are seperated into two daughter cells, and thus equal number of chromosomes is maintained. However, replication does not occur during entire anaphase but is confined only to synthesis (s) phase. There is a post-mitotic gap(G1) between the telophase and S phase. A second premitotic gap (G2) is between the S phase and prophase. Only S phase involves replication process. The G1 phase is most variable and in many eukaryotic cells it is completed within 3 to 4 hours or even months depending on physiological conditions. Mostly DNA synthesis is accomplished in 7 to 8hours. In bacteria growing at long phase, DNA synthesis occurs from the time a cell originates to it give rise to daughter cells. It is networthy that bacteria divide only through binary fission.
In general DNA carries out to important functions such as heterocatalytic function and autocatalytic function. The heterocatalytic function is protein synthesis directed by DNA, and autocatalytic function is the synthesis of its own DNA into replica copies. However replication of DNA in prokaryotes differ from that of eukaryotes.
Leia Mais
REPLICATION Of DNA

one of the most important properties of DNA is that it forms its additional identical copies. The process of forming its replica copy is called replication.Replication is the basis of evolution of all morphologically complexed forms of life. Howard and Pelc demonstrated that in eukaryotes replication occurs during interphase between mitotic cycles and also during interphase are seperated into two daughter cells, and thus equal number of chromosomes is maintained. However, replication does not occur during entire anaphase but is confined only to synthesis (s) phase. There is a post-mitotic gap(G1) between the telophase and S phase. A second premitotic gap (G2) is between the S phase and prophase. Only S phase involves replication process. The G1 phase is most variable and in many eukaryotic cells it is completed within 3 to 4 hours or even months depending on physiological conditions. Mostly DNA synthesis is accomplished in 7 to 8hours. In bacteria growing at long phase, DNA synthesis occurs from the time a cell originates to it give rise to daughter cells. It is networthy that bacteria divide only through binary fission.
In general DNA carries out to important functions such as heterocatalytic function and autocatalytic function. The heterocatalytic function is protein synthesis directed by DNA, and autocatalytic function is the synthesis of its own DNA into replica copies. However replication of DNA in prokaryotes differ from that of eukaryotes.
0
 Here are some important features of genetic code :
Here are some important features of genetic code :
1. sixty one codons correspond to amino acids.
2. Four codons are the signals. There are three stop codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) and one start codon (AUG). Rarely, GUG also acts as start codon.
3. Amino acids with similar structural property consist of related codons, therefore the aspartic acid codons (GAU and GAC) are related to glutamic acid codons (GAA and GAG). Similarly, the codons of phenylalanine (UUU, UUC), tyrosine (UAU, UAC) and tryptophan (UGG) start with uracil. This characteristic of codons facilitates to minimize the effects of mistakes arising during translation or mutagenic base substitution.
4. For many synonym codons specifying the same amino acid the first two bases of the triplet are constant while the third varies. For example, all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCG) specify praline, and all codons starting with AC (ACU, ACC, ACA,ACG) specify threonine. The flexibility in third codon may be to minimize errors.
Leia Mais
IMPORTANT FEAUTURES OF GENETIC CODE
 Here are some important features of genetic code :
Here are some important features of genetic code :1. sixty one codons correspond to amino acids.
2. Four codons are the signals. There are three stop codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) and one start codon (AUG). Rarely, GUG also acts as start codon.
3. Amino acids with similar structural property consist of related codons, therefore the aspartic acid codons (GAU and GAC) are related to glutamic acid codons (GAA and GAG). Similarly, the codons of phenylalanine (UUU, UUC), tyrosine (UAU, UAC) and tryptophan (UGG) start with uracil. This characteristic of codons facilitates to minimize the effects of mistakes arising during translation or mutagenic base substitution.
4. For many synonym codons specifying the same amino acid the first two bases of the triplet are constant while the third varies. For example, all the codons starting with CC (CCU, CCC, CCG) specify praline, and all codons starting with AC (ACU, ACC, ACA,ACG) specify threonine. The flexibility in third codon may be to minimize errors.
0

Moreover, for centuries human being have been altering the genetic make up of organisms by selective breeding of plant and animals. The deliberate modification in genetic material of an organism by changing the nucleic acid directly is called genetic engineering or gene cloning or gene manipulation and is accomplished by several methods which are collectively known as recombinat DNA (rDNA) technology. Recombinant DNA technology begins a new area of research and applied aspects of biology. Therefore, it is a part of biotechnology which is gaining momentum and much boost in recent years.
However, in breeding programmes much work has been done on alteration of nucleotides by several parasexual or conjugation methods indifferent group of organisms. Now –a-day, a large number of mutagenic agents are available that mutate the genes. It is likely that the changed genes may be beneficial, neutral or lethal. Moreover, the conventional breeding programmes are time taking for making sure that the genes have been altered. In contrast, the rDNA technology has solved several problems which hardly or never are possible through the conventional methods.
Gene cloning or genetic engineering can be defined as changing of genes by using in vitro processes. A unified definition of genetic engineering has been given by smith (1996) as the formation of new combinations of heritable material by the insertion of nucleic acid molecules produced by whatever means outside the cell, into any virus, bacterial plasmid or other vector system so as to allow their incorporation into a host organism in which they do not naturally occur but in which they are capper of continued propagation. In brief, gene technology is the modification of the genetic properties of an organism by sing rDNA technology. Genes are like the biological software filled with programme that govern the growth, development and function of organism. By changing in programme of the software it is possible to bring about alteration in the characters of a given organism (smith,1996).
A gene of known function can be isolated from its normal location by biochemical methods in vitro. Moreover, a gene can be synthesized by using gene machine. The isolated genes can be transferred into the microbial cells (that of course do not contain) via a suitable vector. The transferred gene replicates normally and is handed over to the next progeny over generations. After confirmation for its presence through biochemical procedures clone of the same cell is produced.
Leia Mais
GENETIC ENGINERING

Moreover, for centuries human being have been altering the genetic make up of organisms by selective breeding of plant and animals. The deliberate modification in genetic material of an organism by changing the nucleic acid directly is called genetic engineering or gene cloning or gene manipulation and is accomplished by several methods which are collectively known as recombinat DNA (rDNA) technology. Recombinant DNA technology begins a new area of research and applied aspects of biology. Therefore, it is a part of biotechnology which is gaining momentum and much boost in recent years.
However, in breeding programmes much work has been done on alteration of nucleotides by several parasexual or conjugation methods indifferent group of organisms. Now –a-day, a large number of mutagenic agents are available that mutate the genes. It is likely that the changed genes may be beneficial, neutral or lethal. Moreover, the conventional breeding programmes are time taking for making sure that the genes have been altered. In contrast, the rDNA technology has solved several problems which hardly or never are possible through the conventional methods.
Gene cloning or genetic engineering can be defined as changing of genes by using in vitro processes. A unified definition of genetic engineering has been given by smith (1996) as the formation of new combinations of heritable material by the insertion of nucleic acid molecules produced by whatever means outside the cell, into any virus, bacterial plasmid or other vector system so as to allow their incorporation into a host organism in which they do not naturally occur but in which they are capper of continued propagation. In brief, gene technology is the modification of the genetic properties of an organism by sing rDNA technology. Genes are like the biological software filled with programme that govern the growth, development and function of organism. By changing in programme of the software it is possible to bring about alteration in the characters of a given organism (smith,1996).
A gene of known function can be isolated from its normal location by biochemical methods in vitro. Moreover, a gene can be synthesized by using gene machine. The isolated genes can be transferred into the microbial cells (that of course do not contain) via a suitable vector. The transferred gene replicates normally and is handed over to the next progeny over generations. After confirmation for its presence through biochemical procedures clone of the same cell is produced.
0
 For the first time in 1995, Michelson chemically synthesized a dinucleotide in laboratory. Later on in 1970, Har Govind Khorana and K.L. A garwal for the first time chemically synthesized gene coding for tyrosine tRNA are the smallest genes containing about 80 nucleotides. In 1965, Robert w. holley and coworkers worked out first molecular structure of yeast alanine tRNA. This structure lent support to Khorana in deduction of structure of the gene. A gene is responsible for encoding mRNA, and mRNA for polypeptide chain. If the structure of a polypeptide chain is known, the structure of mRAN from genetic code dictionary and in turn the structure of gene can easily be worked out. There are two approaches for artificial synthesis of the gene, by using chemicals and through mRNAs.
For the first time in 1995, Michelson chemically synthesized a dinucleotide in laboratory. Later on in 1970, Har Govind Khorana and K.L. A garwal for the first time chemically synthesized gene coding for tyrosine tRNA are the smallest genes containing about 80 nucleotides. In 1965, Robert w. holley and coworkers worked out first molecular structure of yeast alanine tRNA. This structure lent support to Khorana in deduction of structure of the gene. A gene is responsible for encoding mRNA, and mRNA for polypeptide chain. If the structure of a polypeptide chain is known, the structure of mRAN from genetic code dictionary and in turn the structure of gene can easily be worked out. There are two approaches for artificial synthesis of the gene, by using chemicals and through mRNAs.
Leia Mais
ARTIFICIAL SYNTHESIS OF GENE
 For the first time in 1995, Michelson chemically synthesized a dinucleotide in laboratory. Later on in 1970, Har Govind Khorana and K.L. A garwal for the first time chemically synthesized gene coding for tyrosine tRNA are the smallest genes containing about 80 nucleotides. In 1965, Robert w. holley and coworkers worked out first molecular structure of yeast alanine tRNA. This structure lent support to Khorana in deduction of structure of the gene. A gene is responsible for encoding mRNA, and mRNA for polypeptide chain. If the structure of a polypeptide chain is known, the structure of mRAN from genetic code dictionary and in turn the structure of gene can easily be worked out. There are two approaches for artificial synthesis of the gene, by using chemicals and through mRNAs.
For the first time in 1995, Michelson chemically synthesized a dinucleotide in laboratory. Later on in 1970, Har Govind Khorana and K.L. A garwal for the first time chemically synthesized gene coding for tyrosine tRNA are the smallest genes containing about 80 nucleotides. In 1965, Robert w. holley and coworkers worked out first molecular structure of yeast alanine tRNA. This structure lent support to Khorana in deduction of structure of the gene. A gene is responsible for encoding mRNA, and mRNA for polypeptide chain. If the structure of a polypeptide chain is known, the structure of mRAN from genetic code dictionary and in turn the structure of gene can easily be worked out. There are two approaches for artificial synthesis of the gene, by using chemicals and through mRNAs.
0

The DNA of a microbial cell consists of genes, a few to thousands, which do not express at the same time. At a particular time only a few genes express and synthesize the desired protein. The other genes remain silent at this moment and express when required. Requirement of gene expression is governed by the environment in which they grow. This shows that the genes have a property to switch on and switch off.
20 different amino acids constitute different protein. All are synthesized by
codons. Therefore, synthesis of all the amino acids requires energy which is useless because all the amino acids constituting proteins are not needed at a time. Hence, there is need to control the synthesis of those amino acids which are not required. By doing this the energy of a living cell is conserved and cells become more competent. Therefore, a control system is operative which is known as gene regulation.
Leia Mais
GENE REGULATION

The DNA of a microbial cell consists of genes, a few to thousands, which do not express at the same time. At a particular time only a few genes express and synthesize the desired protein. The other genes remain silent at this moment and express when required. Requirement of gene expression is governed by the environment in which they grow. This shows that the genes have a property to switch on and switch off.
20 different amino acids constitute different protein. All are synthesized by
codons. Therefore, synthesis of all the amino acids requires energy which is useless because all the amino acids constituting proteins are not needed at a time. Hence, there is need to control the synthesis of those amino acids which are not required. By doing this the energy of a living cell is conserved and cells become more competent. Therefore, a control system is operative which is known as gene regulation.
0
GENE EXPRESSION
The DNA has two important role in the cell, first is replication and the second is expression. Gene expression is accomplished by a series of events. The information contained in DNA is converted into molecules that determine the metabolism of the cell.
During the process of gene expression DNA is the first copied into an RNA molecule which determines the amino acid sequences of a molecule of a protein. The RNA molecules are synthesized by using a portion of base sequences of single strand of double stranded DNA. This single strand is called template. Hence formation of an RNA transcript is facilitated by an enzyme, RNA polymerase. Therefore the process of synthesis of an RNA molecule corresponding to a gene is called transcription. By using base sequences and RNA molecule , proteins are synthesized in a definite order. Production of an amino acid sequence from an RNA base sequence is called translation. After completion of translation proteins are synthesized. Therefore, gene expression refers to protein synthesis through two events, transcription and translation.
Leia Mais
During the process of gene expression DNA is the first copied into an RNA molecule which determines the amino acid sequences of a molecule of a protein. The RNA molecules are synthesized by using a portion of base sequences of single strand of double stranded DNA. This single strand is called template. Hence formation of an RNA transcript is facilitated by an enzyme, RNA polymerase. Therefore the process of synthesis of an RNA molecule corresponding to a gene is called transcription. By using base sequences and RNA molecule , proteins are synthesized in a definite order. Production of an amino acid sequence from an RNA base sequence is called translation. After completion of translation proteins are synthesized. Therefore, gene expression refers to protein synthesis through two events, transcription and translation.
0
MICROBIAL GENETICS
In prokaryotes the method of cell division differs from that of eukaryotes. No meiosis or mitosis occurs in prokaryotes because of lack of nucleus. In contrast, in prokaryotes and a few eukaryotic microorganisms most of genetical and molecular works, have been carried out because of easy in handling, fast growth rate, immediate observable characters under any change in conditions and least complex life forms.
Like higher plants and animals, bacteria and the other protists transmit characters to their progenies and in onward generations. Apart from inheritance of characters they also show variability in progenies. These changes are reffered to as phenotype (morphological changes) and genotype (genetic changes). The genotype always remains constant however changes occur through mutation which results in morphological changes or phenotypes in progenies.
In addition, the phenotypic expression depends on the environmental conditions as well. Example is phenotypic changes in agrobacterium radiobacter takes place if it is grown on two different growth media. Mucoid colonies are formed on source salt medium and non-mucoid colonies develop on trypticase soy-agar medium. Secondly yeast produces ethanol when grown in a oxygen deficient conditions, and it is increased its bioms and does not produce ethanol when grown in the presence of sufficient oxygen.
Leia Mais
Like higher plants and animals, bacteria and the other protists transmit characters to their progenies and in onward generations. Apart from inheritance of characters they also show variability in progenies. These changes are reffered to as phenotype (morphological changes) and genotype (genetic changes). The genotype always remains constant however changes occur through mutation which results in morphological changes or phenotypes in progenies.
In addition, the phenotypic expression depends on the environmental conditions as well. Example is phenotypic changes in agrobacterium radiobacter takes place if it is grown on two different growth media. Mucoid colonies are formed on source salt medium and non-mucoid colonies develop on trypticase soy-agar medium. Secondly yeast produces ethanol when grown in a oxygen deficient conditions, and it is increased its bioms and does not produce ethanol when grown in the presence of sufficient oxygen.
0
UNITS OF A GENE
After much extensive work done by the molecular biologists the nature of gene became clear. A gene can be defined as a poly nucleotide chain that consists of segments each controlling a particular trait. Now, genes are considered as a unit of function (cistron), a unit of recombination (recon) and a unit of mutation (muton).
Cistron: A single mRNA is transcribed by a single gene. Therefoer, one-gene-one mRNA hypothesis was put forth. Exceptionally, a single mRNA is also transcribed by more than one gene and it is said to be polycistronic. Therefore, the concept has been given as one-gene-one protien hypothesis. The protiens are the polypeptide chains of amino acids translated by mRNA. Therefore, it has been correctly used as one-gene-one polypeptide hypothesis.
Recon: I n a cistron the recombinational units may be more than one. Thus the smallest unit capable of undergoing recombination is called as recon.
Muton: It may be defined as '' the smallest unit of DNA which may be changed is the nucleotide''. Therefore, cistron is the largest unit in size followed by recon and muton. This can be explained that a gene consists of several cistron, a cistron contains many recons, and a recon a number of mutons. However if the size of a recon is equal to muton, there would be no possibility in recon for consisting of several mutons.
Leia Mais
Cistron: A single mRNA is transcribed by a single gene. Therefoer, one-gene-one mRNA hypothesis was put forth. Exceptionally, a single mRNA is also transcribed by more than one gene and it is said to be polycistronic. Therefore, the concept has been given as one-gene-one protien hypothesis. The protiens are the polypeptide chains of amino acids translated by mRNA. Therefore, it has been correctly used as one-gene-one polypeptide hypothesis.
Recon: I n a cistron the recombinational units may be more than one. Thus the smallest unit capable of undergoing recombination is called as recon.
Muton: It may be defined as '' the smallest unit of DNA which may be changed is the nucleotide''. Therefore, cistron is the largest unit in size followed by recon and muton. This can be explained that a gene consists of several cistron, a cistron contains many recons, and a recon a number of mutons. However if the size of a recon is equal to muton, there would be no possibility in recon for consisting of several mutons.
0
GROWTH OF MICROBES
Growth is defined as an orderly increase in cellular components. Microorganisms grow in a variety of physical and chemical environments. A number of methods are available for microbial growth. The choice depends upon the measurement, objectives and on available techniques usefulness. In some cases of industrial fermentation which contain complex media, indirect methods for estimation need to be used however, no matter what method is used, considerable care is required in interpreting the results. Bacterial growth can be measured either by colony counting or cell counting, weighing cell i.e. cell mass measurement or by cell activity.
Cell mass is directly proportional to cell number. This can be obtained after centrifugation of a known volume of culture and weighing the pellet obtained. This is called fresh weight but dry weight of cells is obtained by drying of the pelleted cells at 90-110 degrees centigrade overnight.
The cell mass and number is also obtained by using optical density method. Turbidity is developed in the liquid medium due to the presense of cells which make cloudy appearence to the eyes. The more the sample, more cells are present, hence more light is scattered. Turbidity can be measured with a photometer or a spectrometer device that detect the amount of unscattered light recorded in photometer unit.
If the concentration of the cell in the sample is high, light scattered away from the detecting unit by one to one cell can be rescattered back by another. Hence, the one to one correspondense between cell number and turbidity does not follow linearity. Secondly, dead cells also interfere during measurement. Hence this method is reasonable accurate only for measurement of microbial growth till early log phase.
Leia Mais
Cell mass is directly proportional to cell number. This can be obtained after centrifugation of a known volume of culture and weighing the pellet obtained. This is called fresh weight but dry weight of cells is obtained by drying of the pelleted cells at 90-110 degrees centigrade overnight.
The cell mass and number is also obtained by using optical density method. Turbidity is developed in the liquid medium due to the presense of cells which make cloudy appearence to the eyes. The more the sample, more cells are present, hence more light is scattered. Turbidity can be measured with a photometer or a spectrometer device that detect the amount of unscattered light recorded in photometer unit.
If the concentration of the cell in the sample is high, light scattered away from the detecting unit by one to one cell can be rescattered back by another. Hence, the one to one correspondense between cell number and turbidity does not follow linearity. Secondly, dead cells also interfere during measurement. Hence this method is reasonable accurate only for measurement of microbial growth till early log phase.
0
CLASSIFICATION OF BACTERIA
Although the bacterial structures are quite simple but their classification is quite difficult. However, due to readily available devices in the field of molecular biology it make the taxonomy much easy.The use of old staining techniques such as Gram's staining for differentiation of bacteria on the basis of cell wall structures, their morphological, biochemical characters for proper characterization were known earlier. The use of molecular biological techniques such as restriction fragment length polymorphism, DNA-DNA hybridization and 16S rRNA sequencing make the studies more easy as far as the phylogeny of the bacterial strains are concerned. As a result there has been a considerable revival of interest in bacterial taxonomy.
The bacterial taxonomy has a rapid and radical change due to involvement of modern molecular biological techniques. This is why it has now refined. Much care has also been taken in ascertaining the history of species so that the species names reflect the original description, rather than a popularly used name.As a result of such activity, the species names assigned to bacteria may change.
The basic constitution of bacterial species is different from higher organism due to the reason that in later forms the species is defined as those which shares many common features and its members breed to produce fertile offspring. While in case of bacteria, they reproduce only asexually by binary fission, hence the above concept does not suit in bacteriology.
The use of computers in bacteriology and in particular taxonomy gave an advantage to resolve the impact of the techniques of numerical taxonomy. This is based on comparing the strains of bacteria for the large number of characters. The more closely related organisms are to have the more characteristics in common. A similarity matrix can be drawn up depicting the degree of relationship between all the species examined and it is then presented in the form of dendogram.
Leia Mais
The bacterial taxonomy has a rapid and radical change due to involvement of modern molecular biological techniques. This is why it has now refined. Much care has also been taken in ascertaining the history of species so that the species names reflect the original description, rather than a popularly used name.As a result of such activity, the species names assigned to bacteria may change.
The basic constitution of bacterial species is different from higher organism due to the reason that in later forms the species is defined as those which shares many common features and its members breed to produce fertile offspring. While in case of bacteria, they reproduce only asexually by binary fission, hence the above concept does not suit in bacteriology.
The use of computers in bacteriology and in particular taxonomy gave an advantage to resolve the impact of the techniques of numerical taxonomy. This is based on comparing the strains of bacteria for the large number of characters. The more closely related organisms are to have the more characteristics in common. A similarity matrix can be drawn up depicting the degree of relationship between all the species examined and it is then presented in the form of dendogram.
0
MICROBIAL DIVERSITY
The current list of the world's biodiversity is quite incomplete and that of viruses, microorganisms and invertebrates is especially deficient. The fungal diversity indicate the total number of species in a particular taxonomic group. The estimates of 1.5 million fungal species is based principally on a ratio of vascular plants of fungi of about 1:6.
Attempts to estimate total numbers of bacteria, archaea, and viruses even more problematical because of difficulties such as detection in and recovery from the environment,incomplete knowledge of obligate microbial associations. The microbial diversity, therefore appears in large
measure of reflect obligate or facultative associations with higher organisms and to be determined by the spatio-temporal diversity of their hosts or associates.
The perception of microbial diversity is being radically altered by DNA technique such as DNA-DNA hybridisation, nucleic acid fingerprinting and methods of assessing the outcome of DNA probing, and perhaps most important at present is 16S rRNA sequencing.
Biological diversity or biodiversity is actually evolved as a part of the evolution of organisms and the smallest unit of microbial diversity is a species. Bacteria due to lack of sexuality, fossil records etc., are defined as a group of similar strains distinguished sufficiently from other similar groups of strains by genotypic, phenotypic, and ecological characteristics.
Leia Mais
Attempts to estimate total numbers of bacteria, archaea, and viruses even more problematical because of difficulties such as detection in and recovery from the environment,incomplete knowledge of obligate microbial associations. The microbial diversity, therefore appears in large
measure of reflect obligate or facultative associations with higher organisms and to be determined by the spatio-temporal diversity of their hosts or associates.
The perception of microbial diversity is being radically altered by DNA technique such as DNA-DNA hybridisation, nucleic acid fingerprinting and methods of assessing the outcome of DNA probing, and perhaps most important at present is 16S rRNA sequencing.
Biological diversity or biodiversity is actually evolved as a part of the evolution of organisms and the smallest unit of microbial diversity is a species. Bacteria due to lack of sexuality, fossil records etc., are defined as a group of similar strains distinguished sufficiently from other similar groups of strains by genotypic, phenotypic, and ecological characteristics.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)





